Vitamin C is essential for a wide range of bodily functions, from strengthening the immune system to aiding collagen production. However, since our bodies can’t store this water-soluble vitamin, a deficiency can sneak up if we’re not mindful of our diet. Many of the symptoms can be subtle at first but grow more serious over time. Knowing these signs can help you spot a potential problem early and take the right steps to correct it through nutrition or supplementation.
1. Frequent Bruising
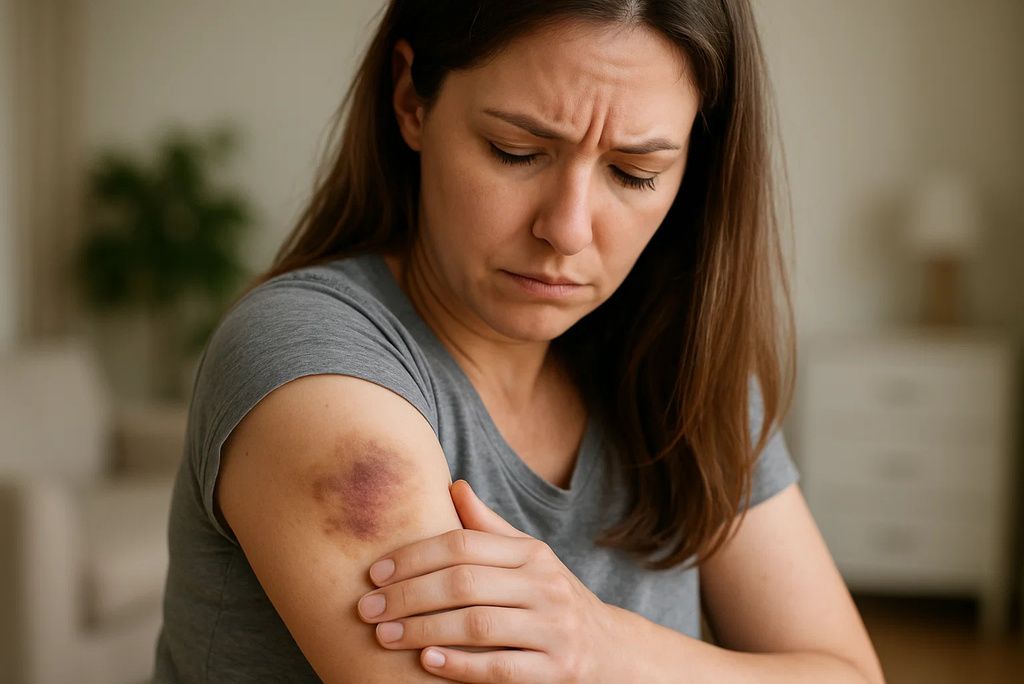
Bruising easily can be one of the first noticeable signs of a vitamin C deficiency. Vitamin C plays a crucial role in collagen synthesis, a protein that strengthens blood vessel walls. Without enough of it, capillaries become fragile, causing blood to leak under the skin from even minor bumps or pressure. If you’ve started to notice unusual bruises on your arms or legs, especially without any clear cause, a lack of vitamin C might be to blame. A study published in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition confirms that low levels of this vitamin are associated with increased bruising risk. (source)
2. Slow Wound Healing
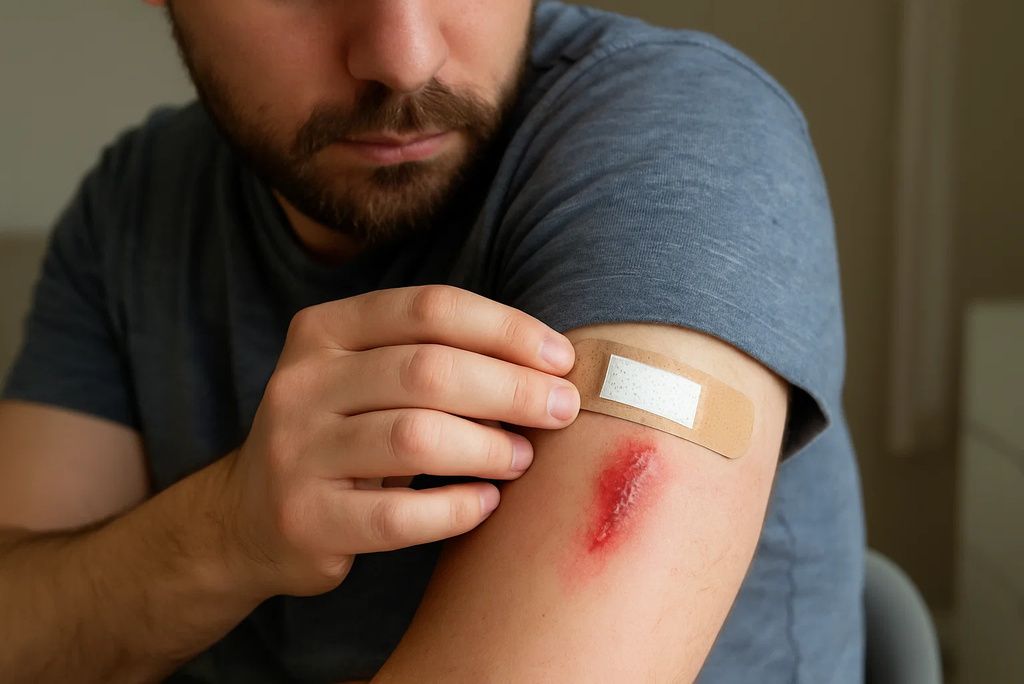
Vitamin C is integral to the body’s natural healing process. It promotes the production of collagen and supports new tissue growth. If cuts or wounds seem to take a long time to heal, or you find that scabs stay on the skin far longer than usual, your body might not be getting enough vitamin C to regenerate properly. In extreme cases, old wounds may even reopen. According to the National Institutes of Health (NIH), delayed healing is a classic sign of vitamin C deficiency. (source)
3. Dry, Splitting Hair and Hair Loss
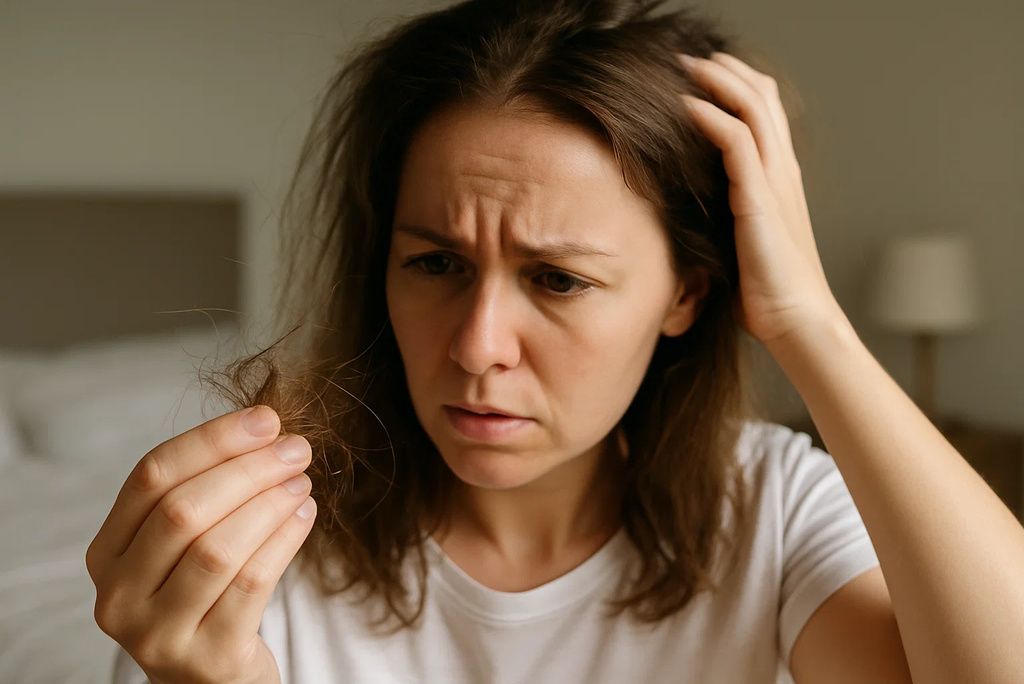

Collagen isn’t just crucial for skin and joints—it also helps support healthy hair. A lack of vitamin C can weaken the hair structure, leading to dry, brittle strands and even hair loss. You might notice more hair in your brush, especially if accompanied by other symptoms like fatigue or irritability. A deficiency also reduces iron absorption, compounding hair health problems. Research in the Dermatology Practical & Conceptual Journal highlights the link between nutrient deficiencies and hair shedding. (source)
4. Persistent Fatigue and Irritability
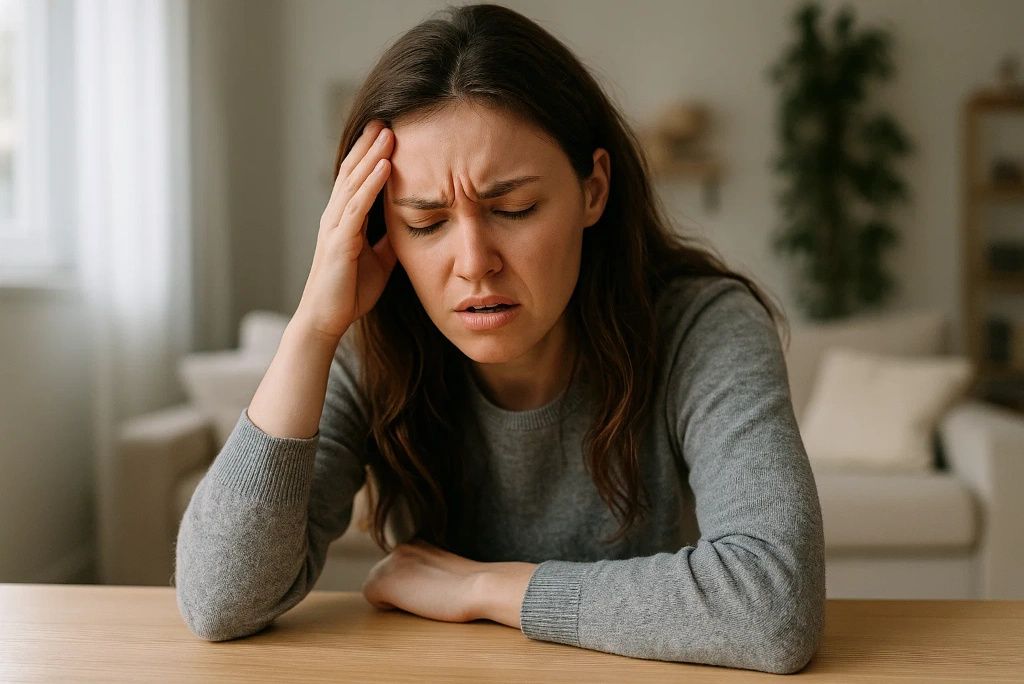

Feeling tired all the time, even with enough sleep? Chronic fatigue is a known symptom of low vitamin C. This nutrient helps convert food into usable energy and supports adrenal function. When deficient, people often report ongoing lethargy, weakness, and irritability. One 2013 study found that vitamin C supplementation in hospitalized patients significantly reduced fatigue levels. (source)
5. Bleeding or Swollen Gums
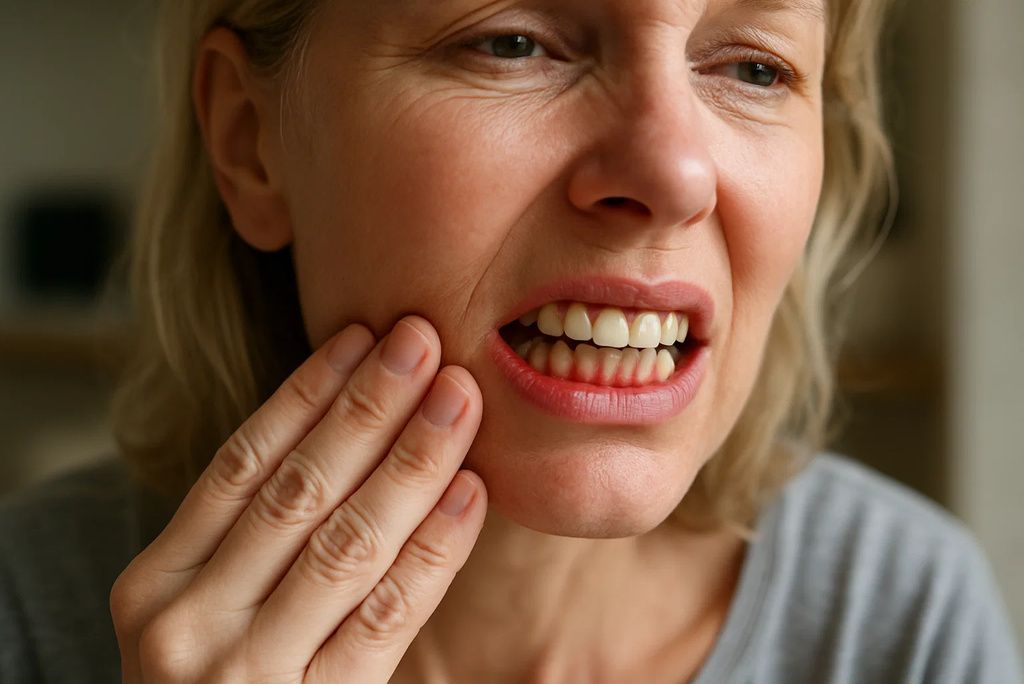
Gum health is directly tied to vitamin C levels. This vitamin maintains the connective tissue in the gums and helps reduce inflammation. When it’s low, gums may bleed during brushing or flossing, appear red and puffy, or even recede. In severe instances, teeth can become loose or even fall out. According to the American Dental Association, vitamin C deficiency remains a cause of periodontal issues today, particularly in diets lacking fresh produce.
6. Rough, Bumpy Skin (Keratosis Pilaris)
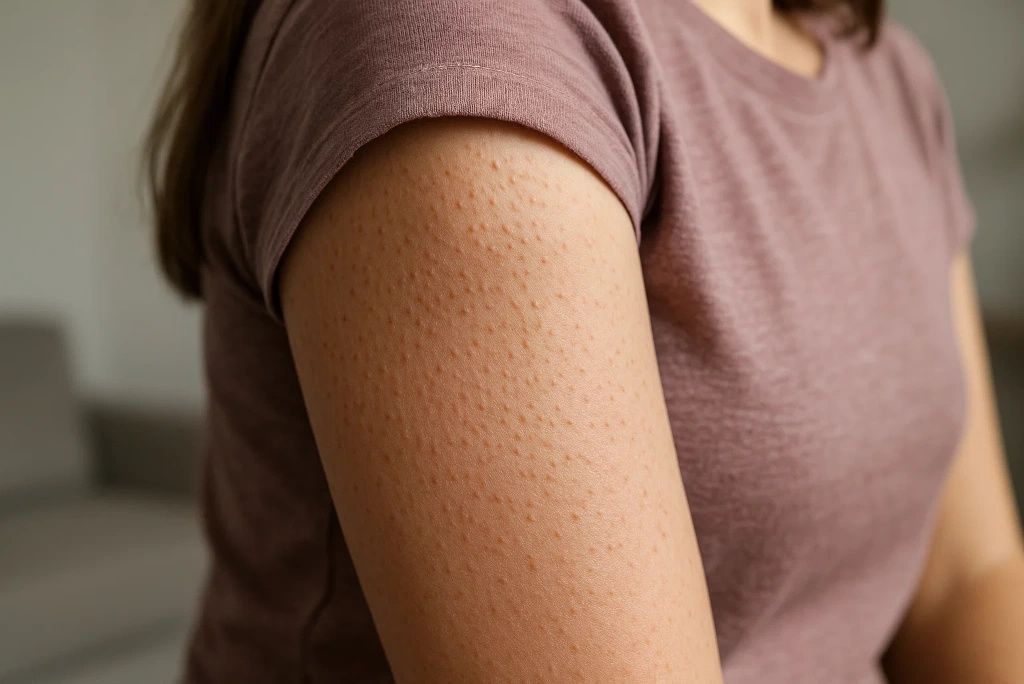

Vitamin C plays a part in keratin metabolism. A deficiency can result in a buildup of keratin in hair follicles, leading to small, hard bumps typically seen on the back of the arms or thighs. This condition, known as keratosis pilaris, is often mistaken for dry skin or eczema. In a 2017 study in the International Journal of Trichology, low levels of vitamin C were linked with various skin manifestations, including keratosis-like conditions. (source)
7. Joint Pain or Swelling

Low vitamin C can lead to joint discomfort or swelling due to its role in collagen maintenance within cartilage and connective tissues. Some individuals may even experience symptoms resembling arthritis. In extreme cases, vitamin C deficiency can result in bleeding inside the joints, causing severe pain. The British Journal of Rheumatology discusses the potential link between hypovitaminosis C and musculoskeletal complaints.
8. Weakened Immune Response

Vitamin C is perhaps best known for boosting immune health. It supports both innate and adaptive immunity by encouraging the production and function of white blood cells. Individuals with low vitamin C often find themselves catching colds, the flu, or other infections more frequently. A review in the Nutrients journal affirms the essential role of vitamin C in immune defense. (source)
9. Iron Deficiency or Anemia

Vitamin C enhances the body’s ability to absorb non-heme iron from plant-based foods. Without it, even an iron-rich diet might not be effective. This can lead to symptoms of anemia, such as weakness, dizziness, and pale skin. The World Health Organization highlights vitamin C’s importance in iron absorption and its potential in addressing global anemia rates. (source)
10. Dry, Scaly Skin
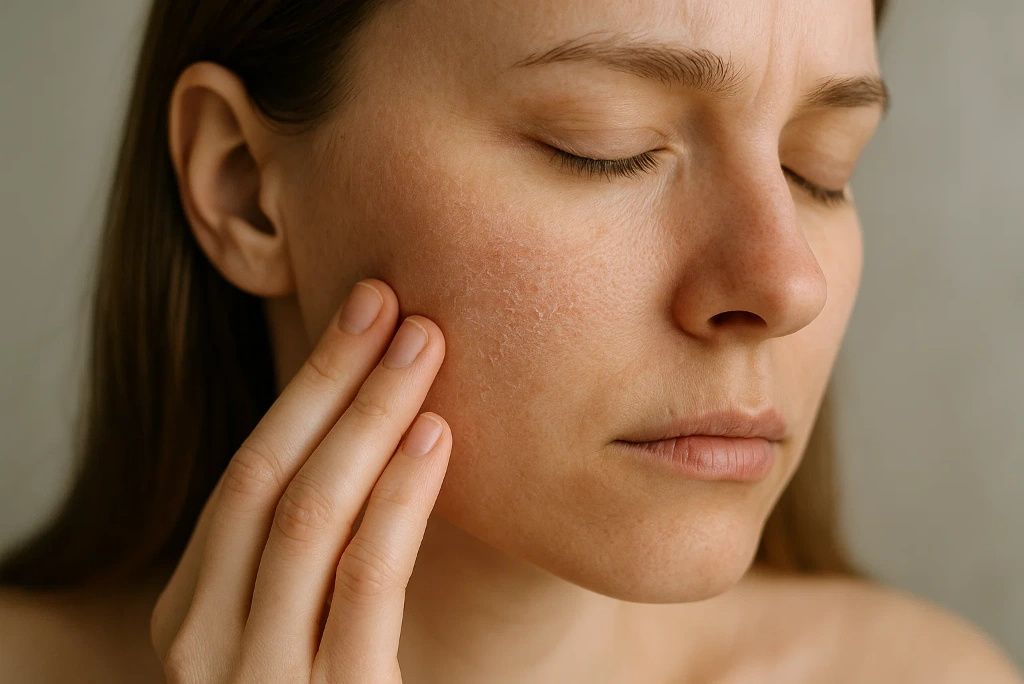

Vitamin C contributes to healthy skin by supporting barrier function and hydration. A deficiency can make your skin feel dry, flaky, and more prone to irritation. It may resemble dermatitis or chronic skin conditions. Research from the Journal of Clinical and Aesthetic Dermatology notes the connection between vitamin C and skin hydration, particularly in patients with compromised skin function. (source)
11. Nosebleeds
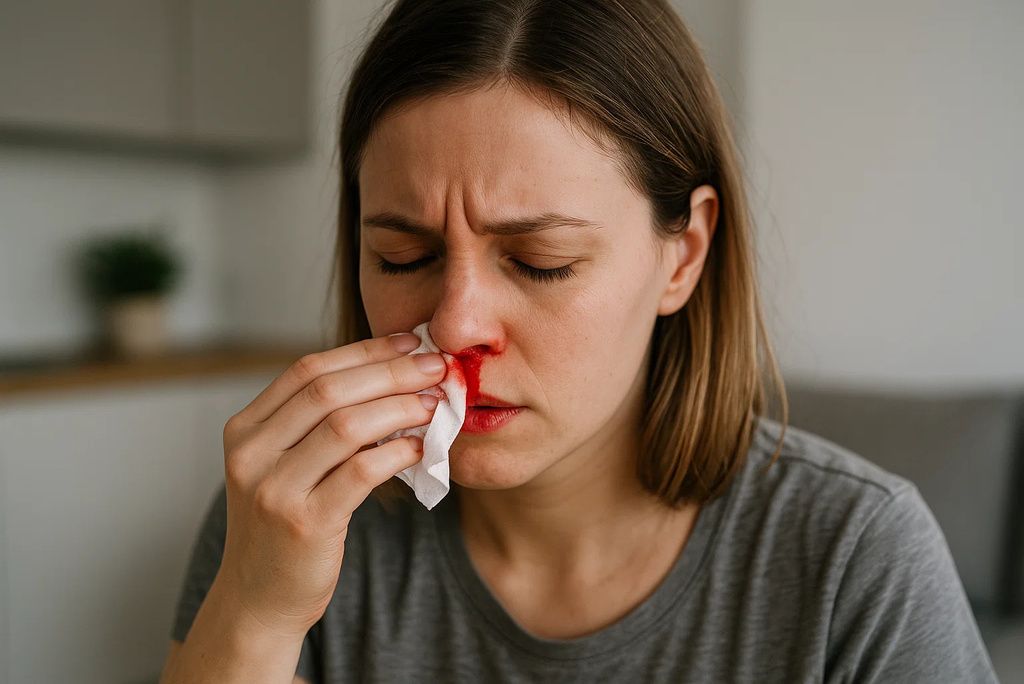

Frequent nosebleeds, especially in dry weather, can be linked to fragile capillaries resulting from low collagen production. Since vitamin C reinforces blood vessels, its deficiency makes nasal tissues more vulnerable to breaks. Studies in Acta Oto-Laryngologica have found a relationship between nutrient deficiencies, including vitamin C, and recurrent nosebleeds. (source)
12. Mood Changes or Depression
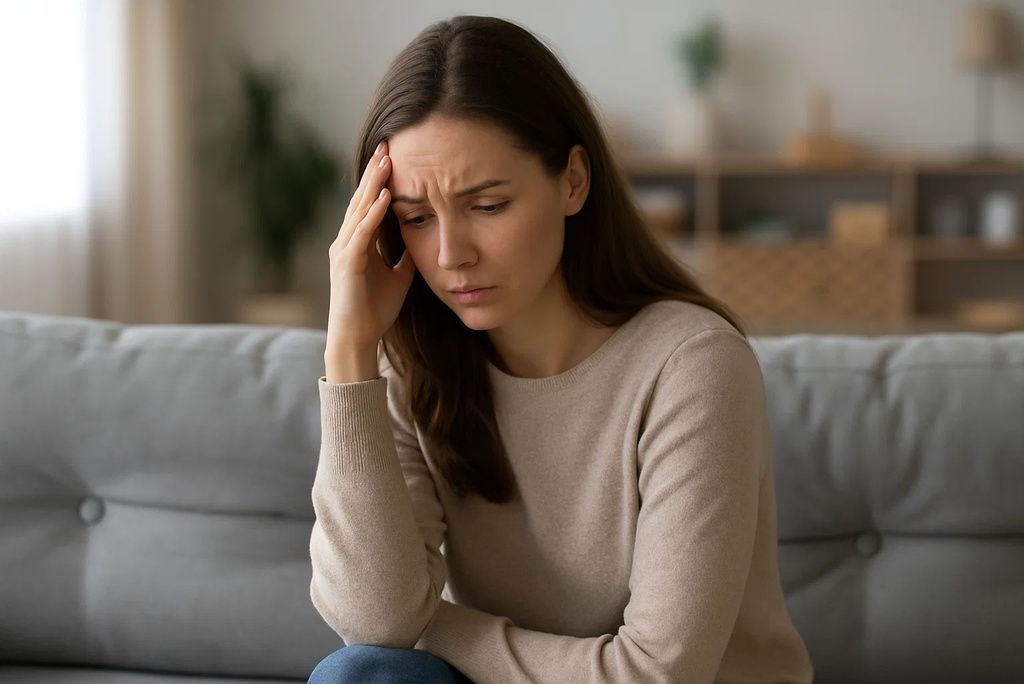

Vitamin C plays a role in synthesizing neurotransmitters like dopamine and serotonin. A deficiency may contribute to symptoms of depression, mood swings, and cognitive sluggishness. A clinical trial from Psychiatry Research found that individuals with low vitamin C levels were more prone to depressive symptoms, which improved with supplementation.
13. Swollen, Painful Joints
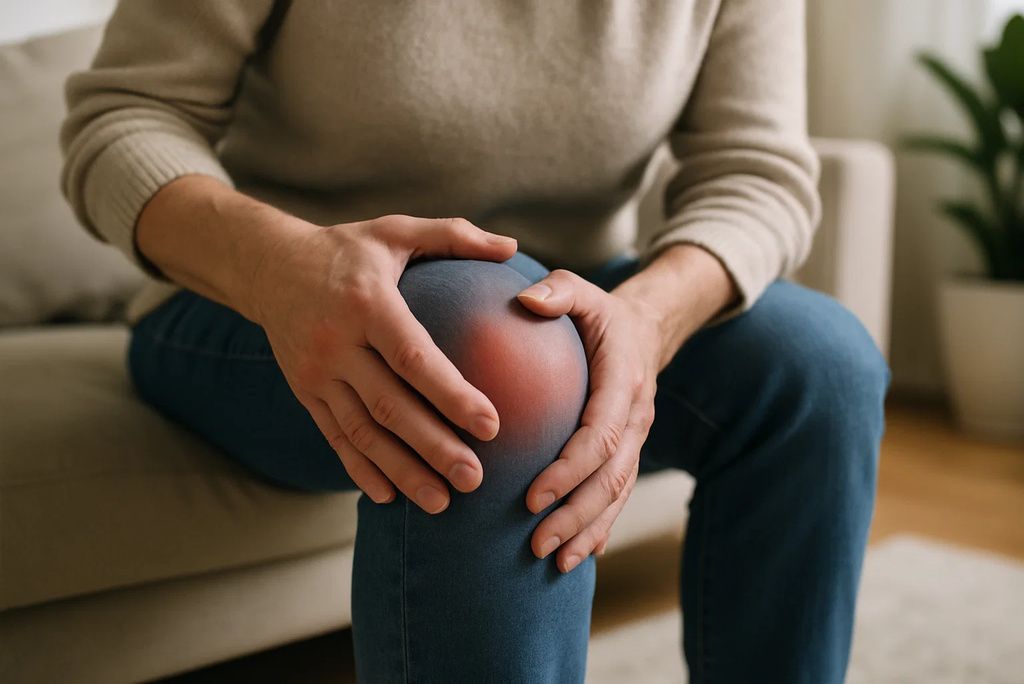

Persistent joint swelling and pain—especially in the knees, wrists, or ankles—can result from vitamin C deficiency. This symptom overlaps with inflammatory arthritis and is often misdiagnosed. The swelling arises due to hemorrhages in joints and weakened cartilage support. A case study in the BMJ Case Reports outlines how vitamin C deficiency led to scurvy-like symptoms, including painful joint inflammation.
14. Tooth Loss
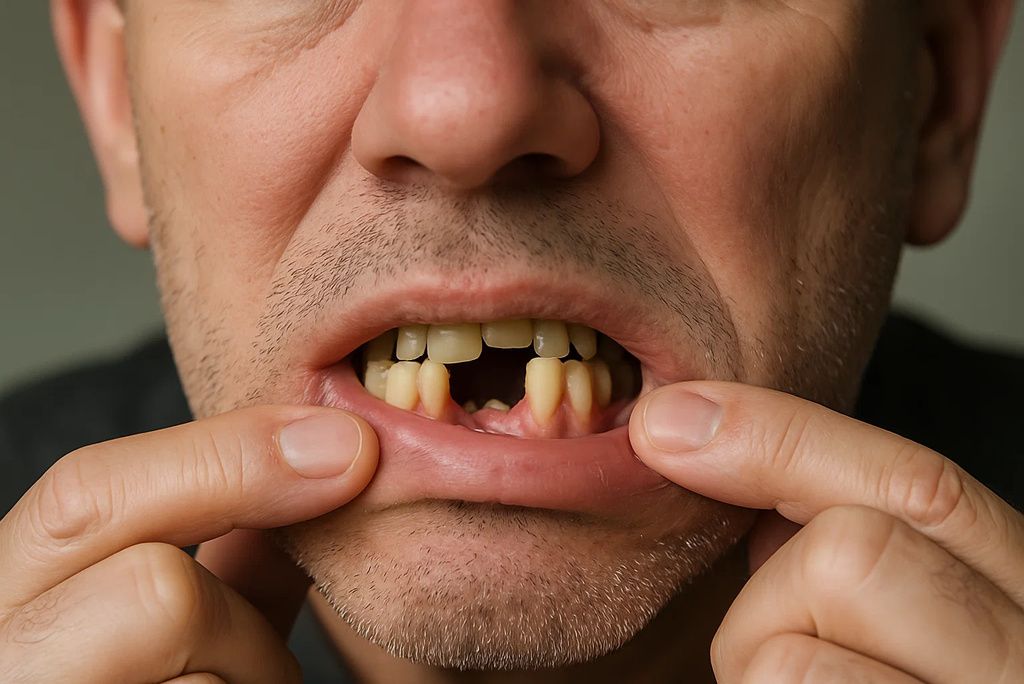
Beyond bleeding gums, vitamin C deficiency can escalate to full tooth loss. The supporting structures weaken without adequate collagen, and teeth may loosen or fall out. This condition was a hallmark of scurvy in historical maritime voyages. Modern cases still occur, particularly in people with highly restricted diets. The Journal of Clinical Periodontology emphasizes the crucial role of vitamin C in dental and periodontal health.
15. Increased Risk of Chronic Diseases

Long-term vitamin C deficiency is associated with elevated oxidative stress and systemic inflammation, factors linked to chronic conditions such as cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and certain cancers. A review in Antioxidants & Redox Signaling details how insufficient vitamin C impairs antioxidant defense, increasing disease susceptibility over time.
Disclaimer: This article is for informational purposes only and does not substitute professional medical advice. Always consult with a healthcare provider for diagnosis or treatment of health conditions.

